મિત્રો, આ Tutorial માં આપણે શીખીશું String handling in java, String in Java, String operation in Java. આ tutorial માં આપણે immutable and mutable string, String creation, String Concatenation and Conversion, changing case of string, string extraction વગેરે શીખીશું.
String Handling in Java
- String handling એ ઘણા બધા concepts provide કરે છે જે string પર perform થાય છે જેવા કે concatenation of string, comparison of string, etc.
What is String?
- String એ double quotes માં લખાતા characters ની sequence છે. ઉદાહરણ તરીકે, “Maricollege”
- જાવા માં string એ object છે.
- String object ને બનાવવા માટે string class નો ઉપયોગ થાય છે.
- String objects એ એક special memory area માં store થાય છે જેને heap memory માં string constant pool કહે છે.
String Creation
- String object બે રીતે create કરી શકાય છે:
- Using string literal
- Using string constructor
Using string literal
- String literal એ double quote “” દ્વારા create થાય છે.
- દરેક વખતે જ્યારે તમે string literal create કરો છો ત્યારે JVM પહેલા memory માં string constant pool ને check કરે છે.
- જો memory pool માં string પેહલેથી જ હશે તો JVM pool કરેલ instance નો reference return કરે છે.
- જો string pool માં exist કરતી નથી તો નવો string object create થાય છે અને pool માં place થાય છે.
Example
String s1 = ”Maricollege”; //નવો object create થયો.String s2 = “Maricollege”; // નવો object create થશે નહિ.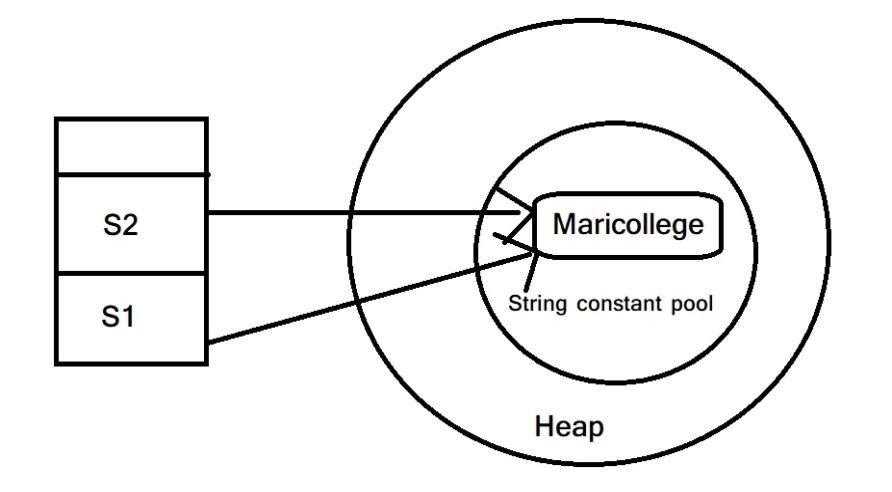
Using string constructor
- આમાં new keyword ની મદદથી string create થાય છે.
Example
1. String s = new String(“Maricollege”);2. String s = new String();3. Char page[] = {‘M’, ‘a’, ‘r’, ‘i’, ‘c’, ‘o’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘e’, ‘g’, ‘e’};
String s = new String(page);Concatenation and Conversion of String
Immutable Strings
- Java માં, string object એ immutable છે.
- Immutable એટલે જેને modify કે change ના કરી શકાય તેવું.
- એકવાર string object create થઈ જાય પછી તેનો data અને state change કરી શકાય નહિ પણ નવો string object બનાવી શકાય.
Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
s.concat(“Hello”);
System.out.println(s); //Maricollege- ઉપરોક્ત example માં માત્ર maricollege જ output મળશે કારણકે string object એ immutable છે.
- આ problem ના solution માટે આપણે reference variable ને explicitly assign કરવું પડે જેથી તે MaricollegeHello ને refer કરે.
Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
s = s.concat(“Hello”);
System.out.println(s); //MaricollegeHelloString Concatenation
- આ case માં, s એ “MaricollegeHello” ને point કરે છે પણ maricollege object modify નથી થયો.
- Java માં string concatenation એ નવી string form છે જે multiple strings નું combination છે.
String concatenation ના બે ways છે:
- Using concat() method
- Using +(string concatenation) operator
Using concat() method
- આ method એ specific string ને current string ના end માં જોડે છે.
Syntax
Public String concat(String object)Example
String s1 = “Mari”;
String s2 = “college”;
String s3 = s1.concat(s2);
System.out.println(s3); //MaricollegeUsing +(string concatenation) operator
- આ operator બે strings ને જોડે છે અને તે string object ને result તરીકે produce કરે છે.
Syntax
String object = “string1” + “string2”;
Example
String s = “Mari” + “college”;
System.out.println(s); //Maricollege- આ operator માત્ર string ને જ નહીં, પરંતુ primitive values ને પણ જોડે છે.
Example
String s = 100 + “maricollege”;
System.out.println(s); //100maricollegeExample
int num = 3;
String s = “This is number” + num;
System.out.println(s); //This is number 3Changing case of string
આમાં બે method નો use થાય છે.
- toLowerCase()
- toUpperCase()
- toLowerCase() માં બધા characters uppercase to lowercase માં convert થાય છે.
- toUpperCase() માં બધા characters lowercase to uppercase માં convert થાય છે.
- Digit જેવા non alphabetical characters પર આની અસર થશે નહીં.
Syntax
String toLowerCase()
String toUpperCase()Example
String s = “MariCOlleGe”;
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()); //MARICOLLEGE
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); //maricollegeCharacter Extraction
- String class એ ઘણી બધી methods એવી provide કરે છે જે string object માંથી characters ને કાઢે છે એટલે કે extract કરે છે.
તે methods નીચે આપેલ છે:
- Substring()
- charAt()
- getChars()
Substring()
- આપેલ string માંથી તમે substring() ની મદદથી string ને extract કરી શકો છો.
- તેના બે forms છે જે syntax માં દર્શાવેલ છે:
Syntax
String substring (int startIndex)
String substring(int startIndex, int endIndex)substring (int startIndex)
- આ form તમને તમે આપેલ startindex થી string ના end સુધીની substring ની copy આપે છે.
substring(int startIndex, int endIndex)
- આ form માં તમને start index થી તમે આપેલ end index સુધી ની substring મળશે.
Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
System.out.println(s.substring(4)); //college
System.out.println(s.substring(0,4)); //MaricharAt()
- આ method string માં specific index એ single character return કરે છે.
Syntax
char charAt(int index)Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
System.out.println(s.charAt(0)); //M
System.out.println(s.charAt(4)); //cgetChars()
- જો તમારે એ સમયે જ એક થી વધારે characters ને extract કરવાની જરૂર છે તો તમે getChars() નો use કરી શકો.
Syntax
void getChars(int start, int end, char target[], int tstart[])
- Start : substring ની શરૂઆત ની index ને specify કરે છે.
- End : substring ની અંત ની index ને specify કરે છે.
- Target[] :array ને specify કરે છે, જ્યાં તમારે characters receive કરવા છે.
- Tstart : substring ની copy કરવા માટે array target[] ની અંદર index ને specify કરે છે.
Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
char target[] = new char[7];
s.getChars(4,11,target,0);
for(int i=0;i<target.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(target[i]); //college
}String length
- String length એ contain થયેલ characters નો number છે.
- તે length() method દ્વારા મેળવી શકાય છે.
Syntax
int length()Example
String s = “Maricollege”;
System.out.println(s.length()); //11String comparison
String class માં બે string ને compare કરવાની ઘણી methods છે.
- equals()
- equalsIgnoreCase()
- compareTo()
- compareToIgnoreCase()
equals()
- આ method, જો string એ same order માં same characters contain કર્યા હોય તો true કરે છે અને ના કર્યા હોય તો false return કરે છે.
- Comparison એ case sensitive છે.
Syntax
boolean equals(String str)Example
String s1 = “Maricollege”;
String s2 = “Maricollege”;
String s3 = “Java”;
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); //falseequalsIgnoreCase()
- આ method case differences ને ignore કરી string comparison કરે છે.
Syntax
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String obj)Example
String s1 = “Maricollege”;
String s2 = “Maricollege”;
String s3 = “Java”;
String s4 = “MARICOLLEGE”;
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); //true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); //false
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s4)); //truecompareTo()
- ઘણી વાર બે strings સરખી છે કે નહીં તે જાણવું પૂરતું નથી.
- Sorting applications માટે તમારે જાણવાની જરૂર છે કે કયું તેના પછીના કરતાં ઓછું, બરાબર અથવા વધારે છે.
- String બીજા કરતાં ઓછી હોય છે જો તે dictionary order માં બીજા કરતાં પહેલા આવે છે.
- String બીજા કરતાં વધારે હોય છે જો તે dictionary order માં બીજા કરતાં પછી આવે છે.
- compareTo() method આ જ purpose માટે use થાય છે.
Syntax
int compareTo(String str)- Comparison નું result integer value માં return થશે.
- ધારો કે, s1 અને s2 બે string variable છે તો:
s1==s2 : 0
s1 > s2 : positive value
s1 < s2 : negative valueExample
String s1 = “Maricollege”;
String s2 = “Maricollege”;
String s3 = “Java”;
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); //3 because s1>s3 àM>J
System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s1)); //-3 because s3<s1 àJ<McompareToIgnoreCase()
- જો તમારે બે string ના comparison વખતે case difference ને ignore કરવો છે તો આ method નો use થાય છે.
Syntax
int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)Example
String s1 = “Maricollege”;
String s2 = “MARICOLLEGE”;
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); //0આ પણ વાંચો – Multi Dimensional Arrays in Java
આ પણ વાંચો – Array in Java – One Dimensional Array
આ પણ વાંચો – Garbage Collection in Java
આ પોસ્ટ જેમાં મિત્રો આપણે જોયું કે String handling in java, String in Java, String operation in Java, immutable and mutable string ,String creation, String Concatenation and Conversion, changing case of string, string extraction.
જો મિત્રો તમને આ પોસ્ટ મદદરૂપ લાગી હોય, તો તમે તમારા મિત્રો સાથે ચોક્કસ શેર કરો અને જો તમને જાવા અથવા બીજા કોઈ વિષય સંબંધિત કોઈ પ્રશ્ન હોય તો તમે નીચે કોમેન્ટ કરીને અમને જણાવી શકો છો. આભાર.
